M&A Report

In evidenza
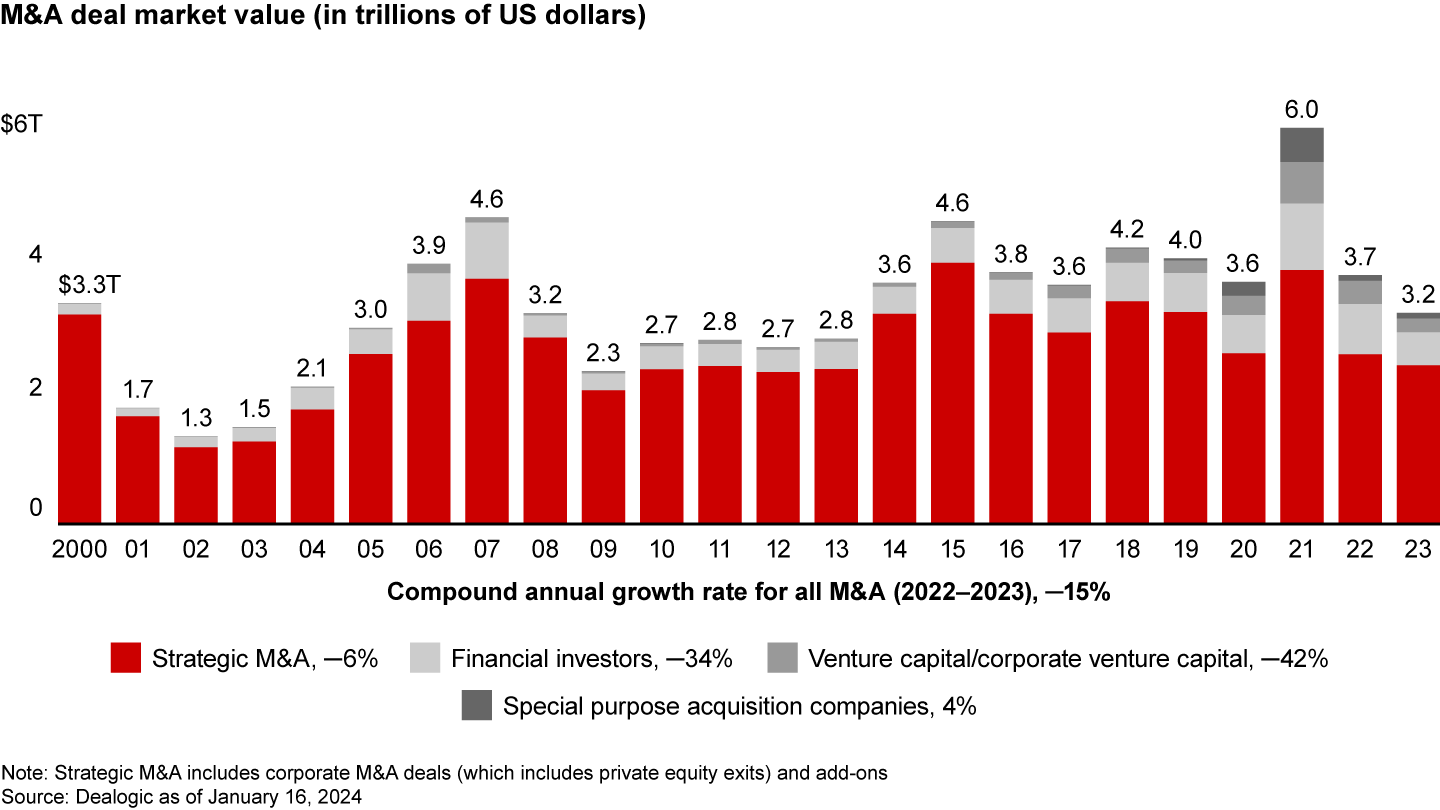
- In 2023, the total M&A market dropped 15%, to $3.2 trillion, the lowest level in a decade.
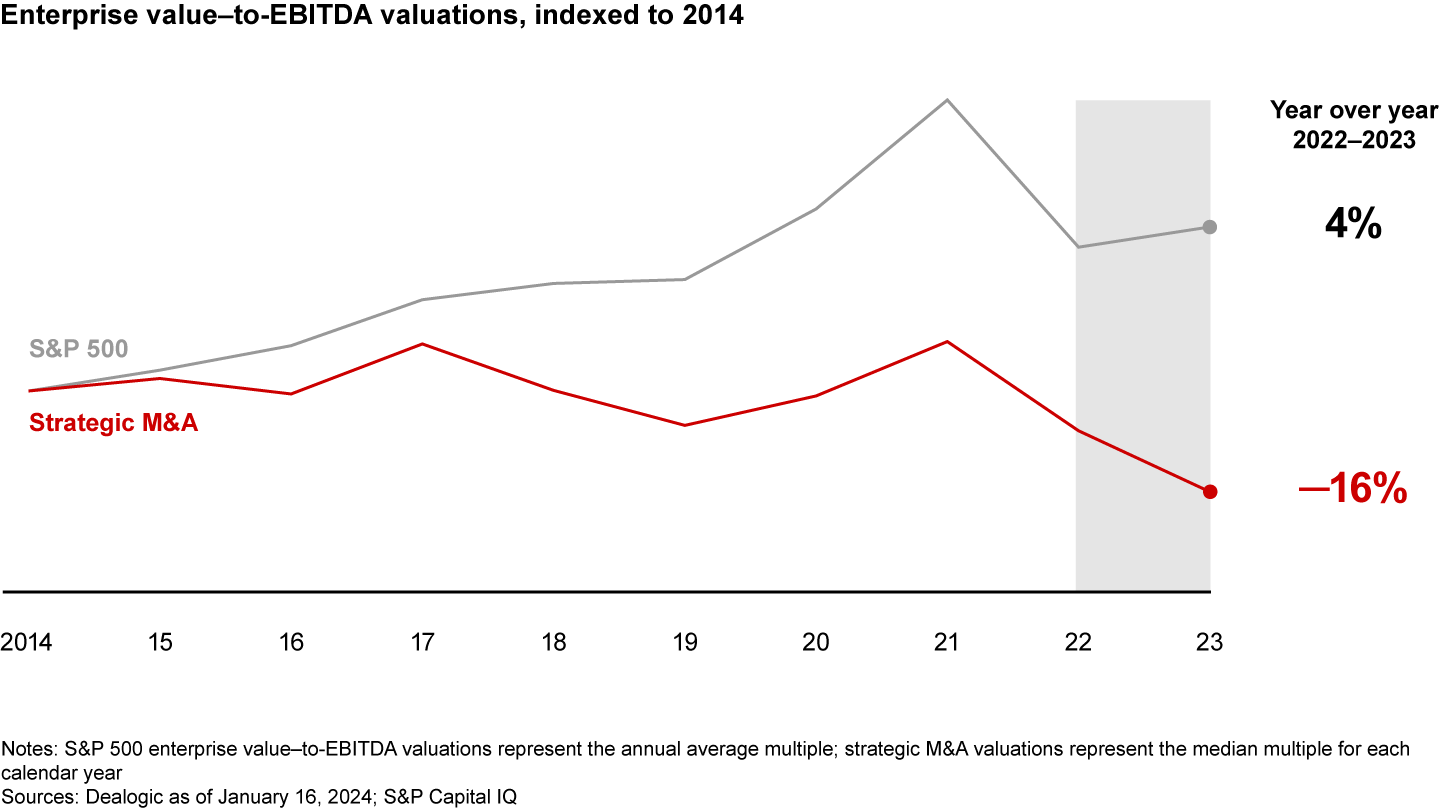
- Strategic M&A declined 6% as buyers and sellers struggled to close the gap on valuations, and strategic deal multiples were the lowest they've been in a decade.
- Deals were delayed for other reasons, including high interest rates, mixed macroeconomic signals, regulatory scrutiny, and geopolitical risks.
- Many longtime frequent acquirers used 2023 as an opportunity to expand their competitive advantage through M&A.
This article is part of Bain's 2024 M&A Report.
It’s no secret that the M&A market declined in 2023 as the valuation gap between what buyers wanted to spend and what sellers wanted to charge for their companies kept many would-be deals from happening. M&A practitioners told us that the valuation gap was the biggest obstacle to dealmaking, and there were other headwinds in 2023 as well, including high interest rates, macroeconomic uncertainty, rising regulatory scrutiny, and new political pressures.
But while down overall by 6% in value, the strategic M&A market reflected uneven performance. For example, tech deals cratered while activity in healthcare and life sciences as well as energy and natural resources rebounded. The Americas market held steady as Europe and Asia faltered. Scratch beneath the placid surface, and you see how, across industries and around the world, winning companies turned to deals to reinvent their future, whether it was automakers acquiring to secure supplies for the transition to electric vehicles, insurers buying to expand their traditional role of risk protection to risk prevention, or media companies learning that partnering with former fierce competitors is the only way to win as their industry enters a new era.
The companies that made such moves will be those that emerge as leaders. Perhaps the most important M&A news from 2023, however, was the widening of the performance gap between frequent acquirers and their inactive peers. According to our long-term research, frequent acquirers always outperform in total shareholder return. In 2023, that margin continued to grow.
What the numbers say
The world of strategic M&A still saw more than 27,000 deals announced, totaling about $2.4 trillion, a 6% decline in value from the year before (see Figure 1). If those numbers seem better than what you may have read in the newspapers, keep in mind that the broader world of leveraged private equity and venture capital deals had a much worse time (down 37% in value). Those businesses were more exposed to the rise of interest rates and issues of debt availability. In contrast, corporate buyers generally had stronger balance sheets with cash on hand to do deals.

Still, no dealmaker could avoid the impact of rising interest rates. Nearly every executive we spoke with and a full 95% of those we surveyed agreed that higher interest rates required them to adapt their approach to M&A in 2023. The No. 1 adjustment? Being more selective in which deals are being pursued, which was cited by two-thirds of respondents.
But the biggest obstacle was the gap between valuations, which contributed to the lowest year for strategic M&A in a decade and caused prices to plunge. The valuation gap was the only thing that surveyed buyers and sellers seemed to agree on. More than two-thirds of buyers told us that it negatively impacted M&A activity. On the other side of the table, at nearly the same rate, potential sellers cited more favorable deal valuations as a top factor in deciding when to bring their assets to market. In some ways, 2023 will be remembered as the year in which buyers and sellers waited for each other to blink.
Anecdotally, we heard from our investment banking friends that a notable number of deal processes were abandoned before bids were accepted this past year. Why was it particularly hard to close the valuation gap in 2023? Our research pointed out four causes.
- Again, rising interest rates played a major role. The big argument throughout 2023 was the shape of the interest rate curve in years to come. Buyers needed deals to deliver a margin of safety from higher-for-longer interest rates whereas sellers held back in hopes that rates would come back down.
- A second straight year of declining strategic deal valuations made dealmakers wary (see Figure 2). At 10.1 times, overall deal multiples were the lowest in 15 years, with room to fall further; most downturns find a trough between 9 times and 10 times. Amid declining valuations, buyers took a skeptical view of assets priced with pride while sellers saw little reason to give away value.
- Moreover, a healthy stock market in 2023 exacerbated the yawning gap between private and public market valuations. With stocks trading well, sellers and their shareholders preferred to hold on to assets rather than face dilution from selling at a depressed multiple.
- Finally, private equity exits were down 44% in value and 22% in volume. Besides cutting off a source of potentially attractive targets, deferred private equity exits meant that there were fewer marks for fair market value, further clouding price transparency.

Another factor behind fewer deals is increased scrutiny by regulators around the globe. The European Commission, the UK Competition and Markets Authority, and the US Department of Justice and Federal Trade Commission have eyed major mergers with skepticism, particularly tech and healthcare tie-ups. A total of $361 billion in deals have been challenged since 2022; most have closed, often with remedies. The dust has not yet settled on the evolving antitrust regulatory landscape as courts weigh in and new guidelines are proposed. National security concerns also remain a factor for sensitive sectors such as semiconductors or nuclear energy. In this environment, some deals may never get off the ground; others are more likely to be abandoned in the face of a challenge. We explore the impact of longer and more uncertain timelines in “Regulation and M&A: How Scrutiny Raises the Bar for Acquirers.”
Looking beneath the surface
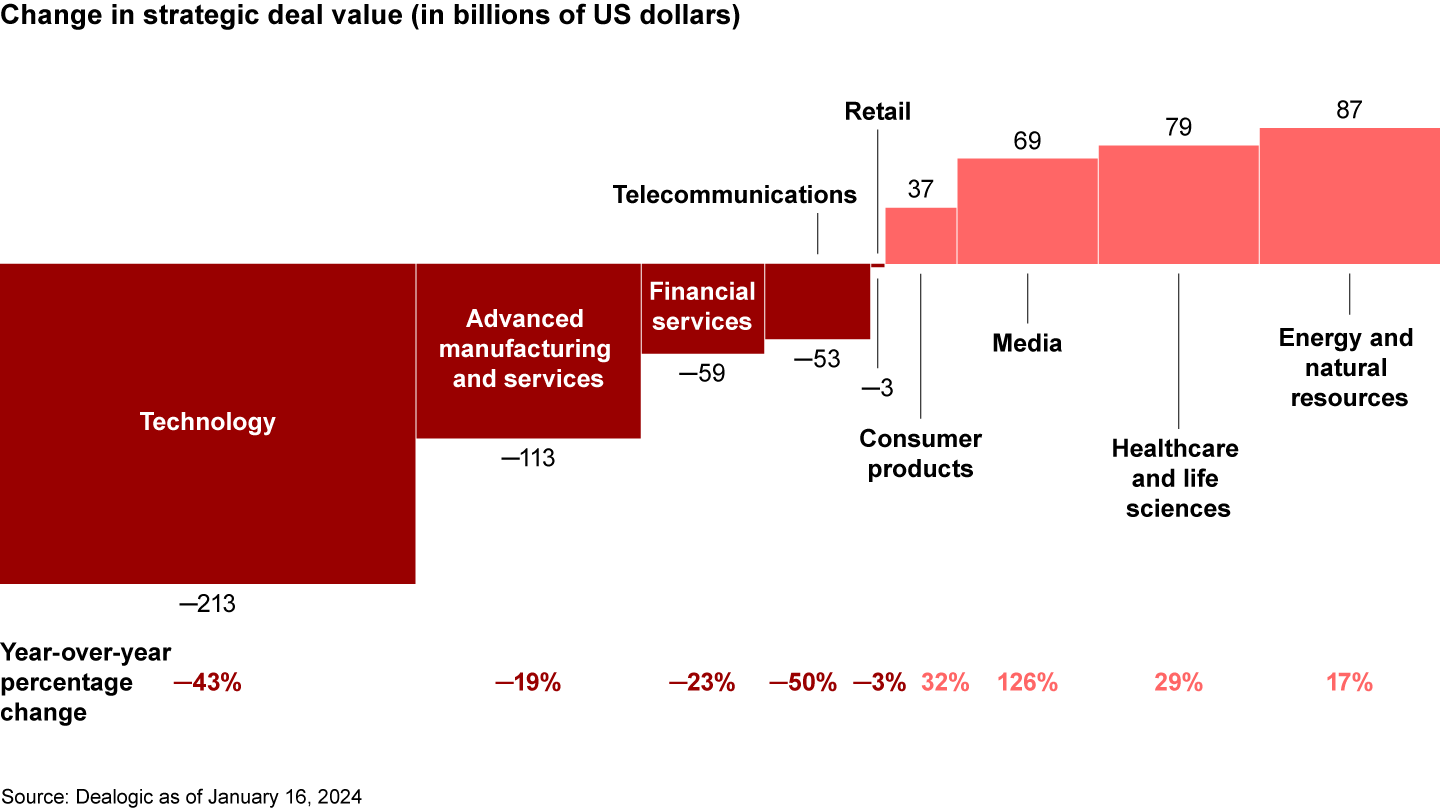
Across industries, the collapse of tech M&A was the biggest drag on strategic M&A in 2023 (see Figure 3). Tech deal values declined by roughly 45% as median valuations, defined by enterprise value–to-EBITDA multiples, tumbled from 2021’s high of 25 times to 13 times last year. Emerson’s acquisition of National Instruments to expand automation capabilities and Cisco’s bid for Splunk for its cybersecurity capabilities point to the ongoing demand for high-quality (and profitable) tech assets. Yet, as we’ve explored elsewhere, a higher-for-longer interest rate environment changes the deal math for most tech deals predicated on growth over profitability (see Global M&A Report Midyear 2022 or M&A Midyear Report 2023: It Takes Two to Make a Market).

At the same time, a healthy dose of big-ticket deals supported a strong M&A year for energy and healthcare, prompted by differing sector dynamics. On the back of rising commodity prices, scale deals in energy and natural resources led the pack, with two megadeals in oil and gas and three additional major tie-ups comprising a total of about $175 billion in deal value, according to Dealogic. Companies in healthcare and life sciences continued their pursuit of growth via scope deals as represented by AbbVie’s back-to-back deals for ImmunoGen and Cerevel Therapeutics in December and Merck’s earlier acquisition of Prometheus.
The year saw a common thread of vertical dealmaking. Companies navigating a shock to the profit pool, whether a shift from internal combustion engines to electric vehicles or the rise of the Internet as a distribution channel, have turned to M&A to transform. Automotive companies are doing deals, such as Stellantis’s investment in Lyten and Ford’s acquisition of Auto Motive Power, to secure access to critical charging technology and to invest in their own recharging grids. In media, the value chain has been redesigned through merging of content and distribution, leading to new strategies for partnerships and alliances.
Vertical M&A can also reflect adaptive strategies in the face of industry consolidation. In the US, healthcare payers are using M&A to build health delivery networks, as exemplified by CVS’s purchase of Oak Street Health this year.
Spin-offs remained an essential tool in portfolio transformation as well. For example, Danaher continued its reorientation toward life sciences via a $23 billion spin-off of its water business (Veralto) while acquiring Abcam and its protein consumables business for $5.7 billion. Sanofi joined other healthcare companies in announcing the separation of its consumer health business. Spin-offs are exceedingly hard to get right, but top-quartile performers show how valuable they can be (see “When a Spin-Off Wins Big”).
Notably, cross-border dealmaking was sustained as investors sought to enhance portfolios in more favorable markets. US buyers pursued more cross-border deals, up 34% in value, while domestic value rose 2%. Similarly, Brazil remained attractive to foreign investment, even as domestic dealmaking declined (see “M&A in Brazil: International Buyers Act While Domestic Acquirers Show Caution”). Asia saw a 60% increase in deals from the Middle East as sovereign wealth funds sought to build supply chains and facilitate energy transitions.
And megadeals made a mark in the second half of 2023, a possible signal that dealmakers were ready to look forward. For M&A observers, the timing wasn’t too surprising. Many companies had sustained high levels of proactive deal screening and outside-in due diligence even as deal counts fell. Some deals, such as Chevron-Hess, were yearslong in the making if opportunistic in timing. Others, such as Carrier’s acquisition of Viessmann Climate Solutions, reflected a bet on long-term trends.
Finally, the year 2023 showed us a widening of the gap between how frequent acquirers and their inactive peers behave in M&A downcycles. You have heard us say more than once that frequent acquirers outperform throughout all economic cycles and tend to stay in the market through good times and bad (see “M&A in Times of Turbulence: Lessons from the Last Recession”). When we look back to the Covid-19 period, for example, we see that most frequent acquirers never stopped doing deals even as the market overall contracted. The same held true with the current market drop that began with the introduction of higher interest rates in June 2022 (see Figure 4). Most frequent acquirers kept acquiring.
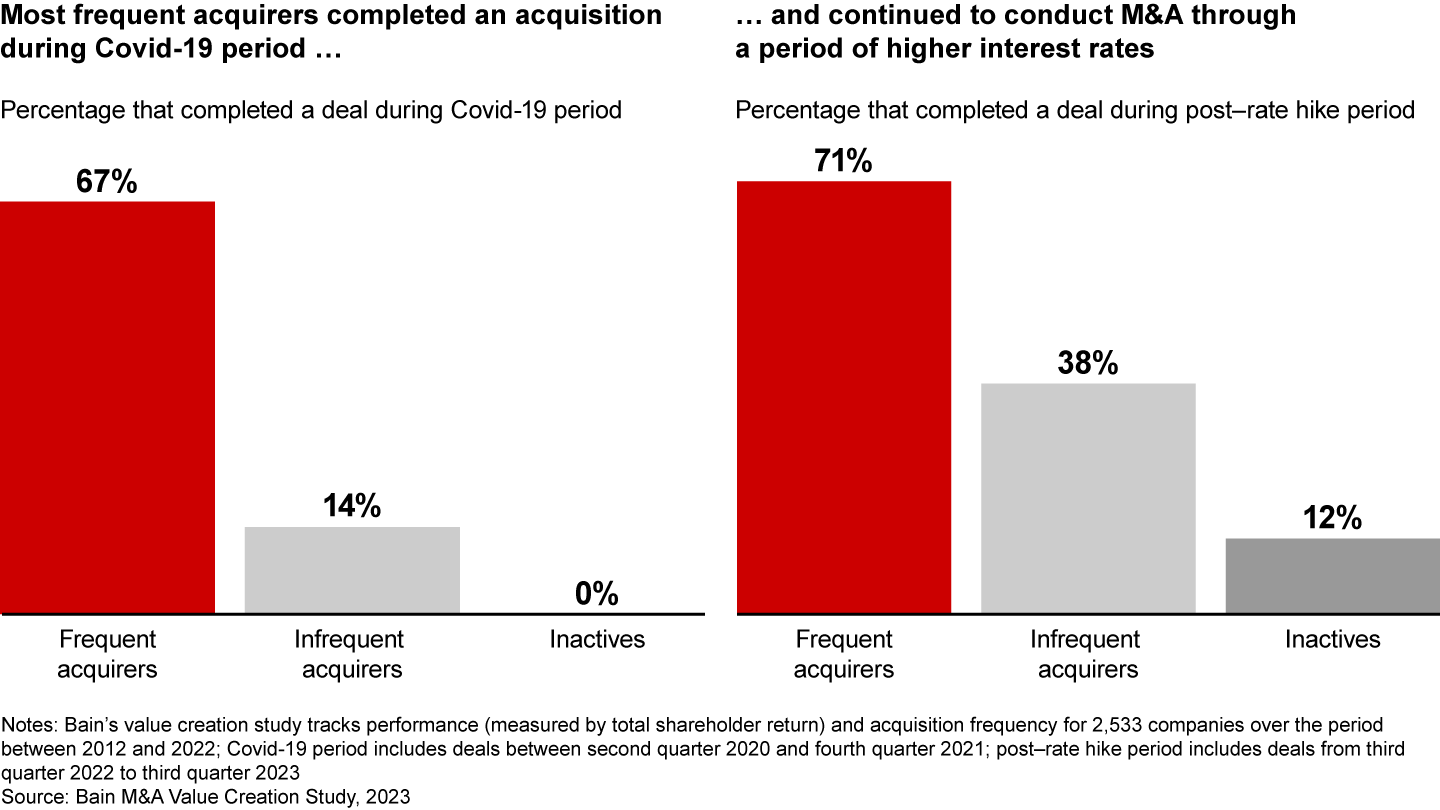

Perhaps counterintuitively, today’s down market signals a longer-term fundamental shift: Those frequent acquirers that stay active are pulling away from less acquisitive or inactive companies as measured by long-term total shareholder returns. Bain research shows that the benefits of frequency are only increasing over time. While others stay on the sidelines, it is companies that invest to acquire through cycles, deploying tested and tailored toolkits to transform their businesses, that ultimately emerge as the winners.
Kudos to frequent acquirers that stay in the game through thick and thin.
In the following chapter, we discuss how the 2023 M&A market dynamic has created a growing backlog of deals that await any sign that buyers and sellers can come to terms.